Munich, October 2025 – With Release 3.2, i-flow opens a new chapter in industrial data integration. The platform becomes both AI-powered and state-aware, combining intelligent automation with real-time data context. Through integrated AI Agents and an entirely new internal State Layer, users can now query live data and events directly from the Unified Namespace (UNS).
“Release 3.2 transforms i-flow into an intelligent integration platform,” says Daniel Goldeband, Managing Director of i-flow GmbH. “Our new AI Agents drastically reduce manual effort in mapping and debugging, while the internal State Layer lays the foundation for a new generation of real-time, logic-driven microservices built on the Unified Namespace.”
AI Agents: Intelligence Built Into the Platform
With Release 3.2, i-flow introduces several new AI Agents that integrate seamlessly into existing workflows. These intelligent assistants automate routine tasks, accelerate troubleshooting, and make knowledge instantly accessible.
The new AI agents at a glance:
- AI Mapping Agent for automated data harmonization: Automates tag mapping between source systems and UNS data models – saves hours of manual work.
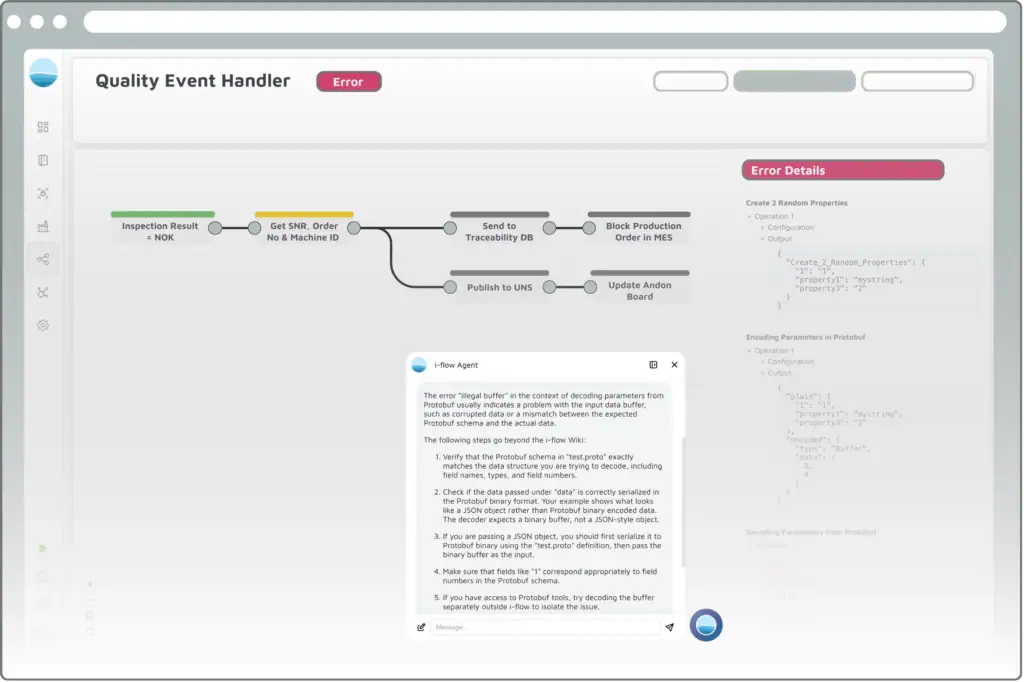
- AI Flow Debugger for accelerated troubleshooting: Explains errors, analyzes causes and suggests step-by-step solutions.
- AI Wiki Agent for quick answers: Answers questions from the official i-flow documentation directly in the app – ideal for onboarding and best practice research.
State Layer: Real-Time Queries in the Unified Namespace
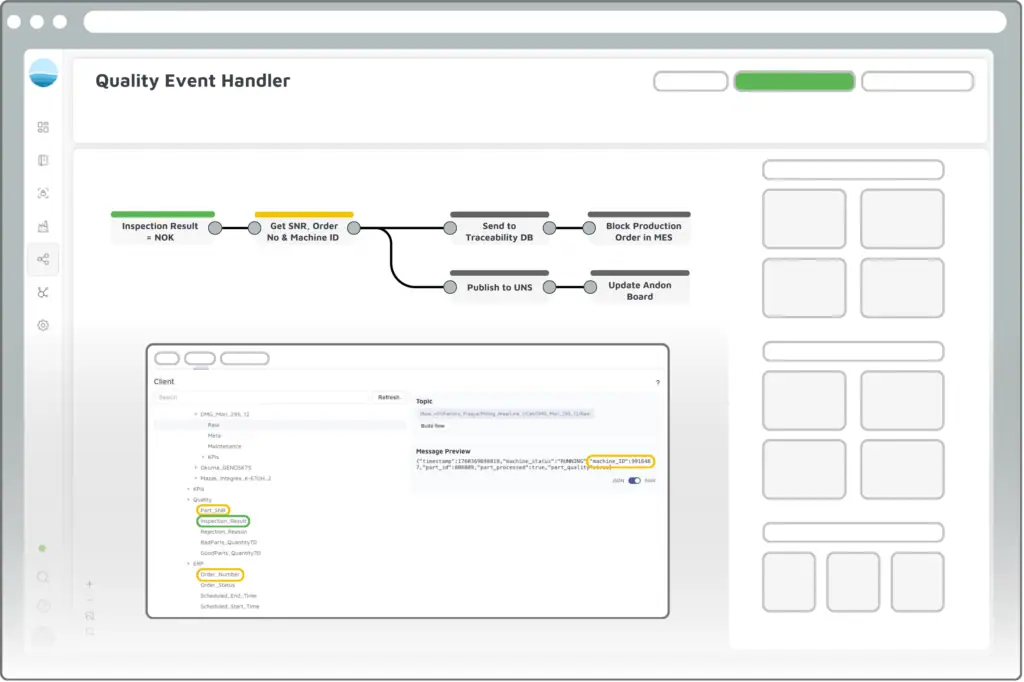
With the new internal State Layer, i-flow introduces a concept of persistent data objects that provide the Unified Namespace with a live, queryable state. This state can be read, subscribed to, or written to in real time — without the need to query source systems directly.
Release 3.2 unlocks a range of new use cases within the Unified Namespace, including:
- State-aware queries: The namespace can be queried dynamically based on OT or IT events. Example: When a machine in a production line enters the Error state, i-flow automatically retrieves the states of all other machines on that line. This helps determine whether the issue is isolated or systemic — enabling coordinated and proactive response strategies.
- Contextualization of events: Process data can be dynamically enriched with serial numbers, order, or machine information from the namespace. Example: If a quality alarm is triggered, i-flow automatically adds the relevant serial number, order, and machine ID to the event. This ensures clear traceability to the affected product and production step, forming the basis for end-to-end traceability and fast root cause analysis.
- Calculation of real-time KPIs: Based on a triggering event, all relevant parameters can be automatically retrieved from the namespace and used for real-time performance calculations. Example: At the end of a production run, i-flow reads parameters such as planned production time, output quantity, and downtime to calculate the current OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) in real time and make it available within the namespace.
Further highlights of the release
- Per-Parameter Source Configurations – Data sources can now be configured individually per parameter. Sampling rates and subscription behavior can be defined for each signal, enabling precise control of data acquisition, reducing unnecessary network load, and improving the overall performance of complex integrations.
- Multi-Connection Assets – i-flow can now retrieve data from multiple source systems in parallel and merge them into a single harmonized data object. This simplifies the integration of heterogeneous data sources — such as machine control, MES, and SCADA systems — and creates a consistent, unified view of production processes.
- Edge Performance Index – The new performance index for edge instances provides a clear assessment of system health and utilization. It allows users to detect performance degradation early as the number of connected systems and throughput increase, ensuring long-term stability and reliability of local edge environments.
More features and details can be found in the release notes.