SAP is widely used in the manufacturing industry. To ensure consistent interaction between business processes and the shop floor, OT data must be reliably integrated into SAP. However, with the discontinuation of SAP MII and SAP Plant Connectivity (PCo), SAP has ended direct OT integration. In addition, traditional point-to-point architectures between OT and IT are increasingly reaching their limits. Against this backdrop, the Unified Namespace (UNS) is emerging as a future-proof integration layer: OT data is provided outside of SAP in an event-driven, decoupled, and contextualized manner. SAP consumes this information selectively via APIs and events. This article compares the SAP interfaces relevant to this architecture.
Overview: SAP, S/4HANA and OT-Relevant Subsystems
SAP is a platform consisting of a core system and connected functional and integration components. In industrial environments, SAP S/4HANA serves as the digital core for transactional business processes such as planning, logistics, quality management, and maintenance. S/4HANA is the successor to the classic SAP ERP (ECC) and is built entirely on the SAP HANA in-memory database. In particular, this database architecture enables S/4HANA to offer significant advantages over R/3 and ECC when processing large volumes of data in parallel.
Overview of OT-Relevant SAP Subsystems
The following overview highlights the most important SAP subsystems relevant in an OT context.
| SAP subsystem | Role in OT context | Status |
|---|---|---|
| SAP Digital Manufacturing (DM/DMC) | Cloud MES for order execution, confirmation, shop floor events | Supported in the long term |
| SAP Integration Suite (CPI) | Middleware for mapping, routing, API and event integration between external systems and SAP applications | Supported in the long term |
| SAP Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) | Maintenance, servicing, notifications, orders, measuring points | Supported in the long term |
| SAP Quality Management (QM) | Quality inspections, inspection lots, quality notifications, release and blocking decisions | Supported in the long term |
| SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) | Intralogistics, warehouse and material flow control (e.g. staging, replenishment, tugger trains, AGVs) | Supported in the long term |
| SAP ME | Classic on-prem MES | ❌ Discontinued |
| SAP MII | Shopfloor Integration & Reporting | ❌ Discontinued |
| SAP Plant Connectivity (PCo) | OT gateway (OPC UA, PLC, fieldbuses) | ❌ Discontinued |
Important Considerations for SAP–OT Integration
S/4HANA is not a real-time system and is not designed to process high-frequency time-series data from the shop floor. As a result, the direct connection of machines and production lines is not part of the ERP core’s responsibility. With the discontinuation of SAP MII and SAP Plant Connectivity (PCo), SAP has also withdrawn from the OT integration space. In modern architectures, OT data is therefore captured outside of S/4HANA via a Unified Namespace (UNS) and made available in an event-driven manner. Solutions such as i-flow form the OT-adjacent backbone, structuring and decoupling machine data and delivering it selectively to SAP systems via APIs or events.
SAP Integration Suite as Middleware
The SAP Integration Suite (CPI) acts as a central middleware layer between SAP systems, cloud services, and external applications. It handles the mapping, routing, and orchestration of APIs and events, thereby decoupling SAP from the technical specifics of connected systems. For this purpose, CPI provides a wide range of native connectors (adapters), including support for REST/OData, SOAP, MQTT, AMQP, JMS, SFTP/FTP, databases, and numerous SAP and cloud services.
In an OT context, CPI is not used for direct machine connectivity, but rather for integration between the Unified Namespace (UNS), event brokers, and SAP systems. Typical scenarios include transforming OT events (e.g., MQTT messages) into SAP-compliant interfaces such as OData services or BAPIs, as well as orchestrating end-to-end business processes across multiple systems.
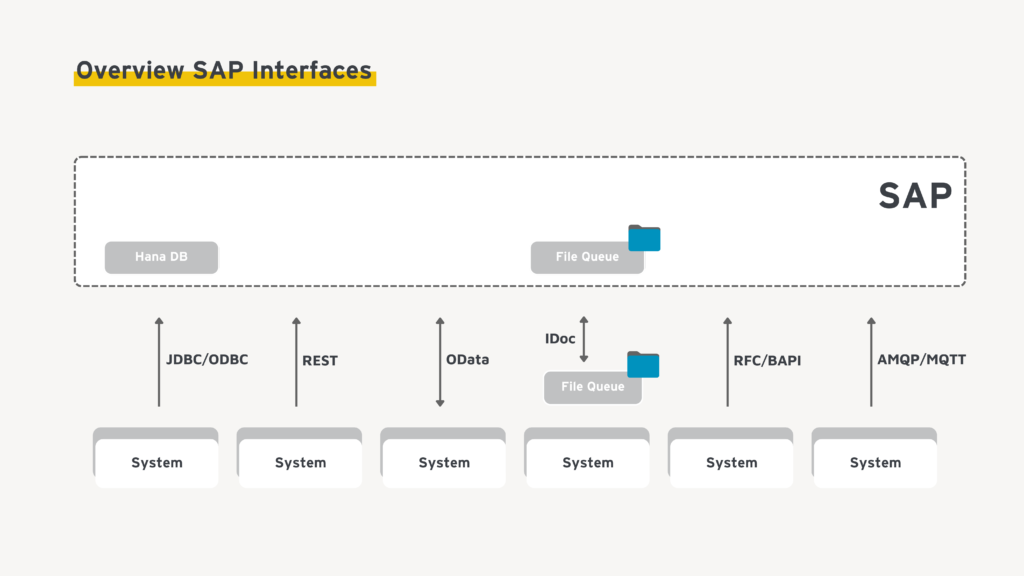
Overview of SAP Interfaces
SAP provides a wide range of technical interfaces for integrating OT and shop floor systems with ERP, MES, and cloud solutions. In production environments, several integration approaches have become established. These approaches differ in their degree of coupling, real-time characteristics, and suitability for cloud-based and event-driven architectures.
1. SAP OData Services (REST APIs)
OData is SAP’s strategic API standard, particularly in S/4HANA and cloud-based scenarios. OData services enable direct access to SAP business objects via HTTP(S), using JSON or XML payloads and standard security mechanisms such as OAuth.
- Typical OT use cases: Synchronous confirmation of production orders, material postings, inventory queries, approvals, or status changes directly from the shop floor.
- Architectural classification: OData is well suited for transactional, near-real-time integrations with modern OT-adjacent software such as MES solutions, IIoT platforms, and mobile applications. However, OData is not suitable for large data volumes or high-frequency sensor data. In such cases, asynchronous, event-driven SAP interfaces are the preferred approach.
- Required expertise: REST/OData, OAuth and identity management, SAP API and business object models, error handling and retry mechanisms.
2. SAP Digital Manufacturing (DMC) APIs
SAP Digital Manufacturing consistently relies on cloud-native REST APIs, events, and webhooks to integrate shop floor data.
- Typical OT use cases: Order and confirmation data exchanged via APIs, event-driven notifications for production or quality-related events, and integration into Unified Namespace (UNS) and broker-based architectures.
- Architectural classification: DMC APIs are highly scalable and cloud-ready, but require well-defined API, event, and security designs (OAuth, topic structures, governance). They represent a shift from purely transactional interfaces toward event-centric SAP integration patterns.
- Required expertise: Cloud and API design, OAuth, event and webhook design, topic structures, and governance concepts.
Differentiation between SAP OData Services and DMC REST APIs
| Aspect | S/4HANA | SAP Digital Manufacturing (DMC) |
|---|---|---|
| API Standard | OData as the main standard | REST Endpoints + (non-OData) |
| Focus | ERP transactions & business objects | Process/MES data & production events |
| Real-time capability | synchronous/transactional | synchronous & asynchronous (events/webhooks) |
| Typical use | Production orders, status, material data | Shop floor status, quality/production events |
| Integration with UNS/Event Mesh | possible via APIs/Events | natively event-friendly |
3. Direct Database Access to SAP S/4HANA
SAP S/4HANA is built on an in-memory database that, in on-premise and private cloud editions, technically allows direct access by external systems via JDBC or ODBC. This type of access is primarily suited for read-only scenarios, such as analytics, reporting, or the extraction of production and transactional data.
- Typical OT use cases: Read-only access to production, movement, or status data for reporting and analytical purposes outside the SAP system.
- Architectural classification: Direct database access is not a standard SAP integration mechanism, but rather a technical access path. Read-only access—ideally via released CDS views—can be appropriate in selected scenarios. Write access, however, bypasses SAP business logic, validations, and security controls and is therefore neither upgrade-safe nor operationally supported. For write operations, only official SAP interfaces such as OData APIs, BAPIs, or event-driven mechanisms should be used.
- Required expertise: SQL and SAP HANA, SAP data model knowledge, CDS views, security concepts, and read-only governance.
4. SAP IDoc (Intermediate Documents)
IDocs are SAP’s traditional format for structured, asynchronous message exchange. They are processed internally as data records and can be exchanged between SAP and external systems via various transport mechanisms, such as RFC, middleware platforms, or, in some cases, file-based transfer.
- Typical OT use cases: Plant-to-ERP integration (e.g., production order confirmations), master data distribution (material masters, bills of materials, routings).
- Architectural classification: In practice, IDocs are often transported in a file-based manner via additional middleware components such as FTP servers or EDI gateways. This multi-step transmission increases integration complexity and susceptibility to errors, particularly in the case of network issues or limited end-to-end visibility. Furthermore, IDocs are not suitable for real-time processing. In cloud-based architectures, especially in the SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud, they are therefore increasingly being replaced by API-first approaches. Nevertheless, IDocs remain a foundational element in many established brownfield SAP landscapes.
- Required expertise: IDoc types and mapping (e.g., MATMAS, LOIPRO), ALE and EDI fundamentals, monitoring and reprocessing.
5. SAP RFC / BAPI
RFC (Remote Function Call) and BAPI (Business Application Programming Interface) enable direct, synchronous function calls in the SAP backend, offering high performance and full transactional consistency.
- Typical OT use cases: Time-critical postings from MES solutions or integration middleware, production confirmations, quality and production bookings, and existing brownfield integrations with high transaction volumes.
- Architectural classification: RFC/BAPI is technically efficient but requires tight, proprietary coupling to the SAP system. It also depends on specialized connectors (supported by i-flow). In modern cloud-based and Unified Namespace (UNS) architectures, this type of SAP interface is increasingly being supplemented or replaced by API- and event-based integration patterns.
- Required expertise (very high): ABAP and BAPI development, function modules, SAP data and document logic, authorization concepts, and error and lock handling.
6. SAP Message Queues / Event Mesh
SAP Event Mesh is a key building block for event-driven SAP integration. As a cloud-based message broker, it supports publish/subscribe communication models using protocols such as AMQP and MQTT.
- Typical OT use cases: Near-real-time distribution of business and shop floor events, integration with a Unified Namespace (UNS).
- Architectural classification: SAP Event Mesh enables loose, event-based coupling between SAP systems and external applications. After authentication, external systems can publish events to, or subscribe to events from, the broker using protocols such as MQTT or AMQP. This makes Event Mesh suitable not only for distributing SAP business events, but also for integrating OT-generated events. While it is well suited for scalable, asynchronous communication, it is not designed for synchronous, transactional postings.
- Required expertise: Event-driven architecture principles, MQTT and AMQP, topic design, security (OAuth, TLS), and schema and event governance.
Using SAP Interfaces Correctly: Use Case Overview
The following overview assigns the most important SAP interfaces to typical integration scenarios and shows which technologies are suitable for specific data flows, degrees of coupling, and architectural patterns.
| SAP interface | Brief description | Strengths & limitations | Typical integration scenarios (examples) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OData Services (REST APIs) | Standardized web APIs on SAP business objects (HTTP(S), OAuth, JSON/XML) | Strengths: API-first, cloud-enabled, well suited for transactional postings in S/4HANA. Limitations: Unsuitable for mass data and high-frequency signals; requires clean API and authorization design. |
Transactional posting of transaction data (order confirmations, material postings, status changes); Retrieve master data on-demand (material master, routings). |
| SAP Digital Manufacturing (DM/DMC) APIs | Cloud-native REST APIs plus events/webhooks for shop floor and MES processes | Strengths: Highly scalable, event and cloud-capable, well suited for UNS and broker architectures. Limitations: Requires clear event, topic and security governance; more process-oriented than object-oriented. |
Cloud MES integration (orders, confirmations); Events for production and quality events; Coupling to UNS via event broker. |
| Direct DB access (JDBC/ODBC, read) | Technical read access to S/4HANA database (on-prem / private cloud), ideally via CDS views | Strengths: Very efficient for reporting and data export (read-only). Limitations: No official integration mechanism; write access not upgrade- or operationally supported; deployment-dependent. |
Reporting and analytics outside SAP; Data export for BI or Datamart solutions (read-only). |
| IDoc (Intermediate Documents) | Classic, asynchronous and structured message transfer (e.g. via RFC, middleware, file) | Strengths: Robust, proven in brownfield scenarios, good for large volumes of data and master data packages. Limitations: Not near-real-time; often multi-level and complex; sometimes not available in cloud editions. |
Master data distribution (material master, bill of materials, routings); ERP-MES links (e.g. LOIPRO, periodic confirmations). |
| RFC / BAPI | Direct, synchronous function calls in the SAP backend with high transaction security | Strengths: High performance and transaction security, suitable for timely postings in on-prem scenarios. Limitations: Proprietary, high operating costs, not very cloud-native, tight coupling. |
Time-critical production and quality postings; Existing MES-SAP integrations with high transaction density (brownfield). |
| SAP Event Mesh (Pub/Sub) | Cloud broker for event-based integration (MQTT/AMQP, publish/subscribe) | Strengths: Loose coupling, high scalability, ideal as an event and UNS backbone. Limitations: Not suitable for synchronous bookings; requires a clean topic and event governance model. |
Distribution of events such as “OrderReleased”, “QualityResult”, “DowntimeDetected” to multiple systems; Forwarding of selected OT events from the UNS to cloud SAP landscapes. |
From Interface to Architectural Decision
The SAP interfaces presented differ significantly in their degree of coupling, communication model, and cloud readiness. However, none of these technologies is inherently “right” or “wrong.” In practice, multiple interfaces are often used in parallel—each where it makes technical and architectural sense. The decisive factor is therefore not an isolated evaluation of individual SAP technologies, but rather the question of which type of data flow should be handled by which integration approach. This classification is central to a stable SAP–OT architecture, especially in the context of a Unified Namespace (UNS).
Near-real-time vs. batch
In SAP environments, true real-time processing in the millisecond range is rarely required. Instead, the key distinction is between near-real-time processing (seconds) and batch-oriented processing.
RFC/BAPI and OData APIs are particularly well suited for near-real-time scenarios, as postings can be executed directly and selectively in the SAP backend. These interfaces are transactional by design and provide immediate business feedback—for example, for status changes, confirmations, or quality-relevant postings from the shop floor. Differences in technical overhead are typically secondary to semantics, consistency, and transactional integrity.
Event Mesh also addresses near-real-time requirements, but with a different focus: events are distributed asynchronously and in a decoupled manner, typically within a few seconds. This makes the approach especially suitable for informing multiple systems in parallel without performing immediate postings in SAP—a core architectural principle of Unified Namespace–based integrations.
IDocs, by contrast, are clearly batch-oriented. They are processed with a time delay (for example, in minute- or hourly-based intervals) and are designed for robustness and large data volumes, rather than for time-critical feedback.
Practical guideline: Whenever an event must take effect promptly—such as in the case of faults, releases, or immediate status postings—API- or BAPI-based integrations are the preferred choice.
Asynchronous vs. synchronous
Another key differentiator among SAP interfaces is the communication model.
Synchronous interfaces such as RFC/BAPI or OData APIs expect an immediate response from the SAP system. The calling process instantly knows whether a posting was successful or failed. This is ideal for critical business processes that require immediate feedback, such as order confirmations, status changes, or quality-relevant postings.
Asynchronous interfaces such as Event Mesh or IDocs decouple sender and receiver in time. The producer of an event does not wait for processing in SAP, but instead provides information that SAP or other systems consume later. This model significantly increases scalability and architectural robustness, as load peaks can be absorbed and systems can continue operating independently.
Master data vs. transaction data:
Another key criterion for selecting the appropriate SAP interface is the type of data being integrated. Master data and transactional data differ fundamentally in terms of change frequency, data volume, and time criticality—and therefore impose different integration requirements.
Master data such as material masters, bills of materials, or routings change relatively infrequently. As a result, they can be bundled and transferred periodically. In many existing architectures, IDoc-based integrations are still used for this purpose, for example for regular synchronization between ERP and MES systems (e.g., MATMAS, BOMMAT). Alternatively, master data can be provided on demand via OData APIs, for instance when a shop floor system or machine explicitly requests information about a material or routing. In these scenarios, consistency and completeness are more important than immediacy.
Transactional data, by contrast, is generated continuously during ongoing production processes—such as production orders, quantity confirmations, quality measurements, or status changes. This data is often time-critical, processed individually, and has a direct impact on operational processes. Accordingly, transactional interfaces such as BAPIs or OData APIs are suitable for targeted postings, while event-driven approaches are well suited for distributing this information across systems.
On-prem vs. cloud SAP
In addition to timing behavior, communication model, and data type, the deployment model of the SAP system plays a decisive role in selecting the appropriate interface. Whether SAP is operated on premise or delivered as a cloud service directly influences which integration mechanisms are technically available and architecturally viable.
In traditional on-premise landscapes—such as SAP ECC or S/4HANA On-Premise combined with local MES and shop floor IT—RFC/BAPI and IDocs have historically been the primary integration mechanisms. These interfaces are tightly integrated with the SAP backend, provide high transactional reliability, and do not require additional cloud infrastructure. As a result, they remain widely used and functionally proven, particularly in brownfield environments.
With the transition to cloud-based SAP systems (such as S/4HANA Cloud or SAP Digital Manufacturing), the integration focus shifts significantly. In cloud editions, web APIs (OData/REST) are the primary—and in some cases the only—supported integration option. Traditional mechanisms such as RFC or IDocs are only partially available or not available at all, depending on the cloud variant (for example, in SAP S/4HANA Public Cloud). Cloud-based SAP therefore effectively enforces an API-first integration approach.
Best Practices
A number of architectural principles can be derived from the interfaces and data flows described above. They make SAP–OT integrations maintainable, secure, and scalable.
1. Decoupling instead of point-to-point integration
Point-to-point connections between OT and IT scale poorly: every additional machine or application increases integration effort disproportionately. Instead, rely on publish/subscribe. A messaging layer—on the shop floor or in the cloud—decouples producers and consumers. Systems publish data without knowing who will consume it. This increases robustness, simplifies expansion, and prevents SAP from being burdened multiple times by the same data. Event meshes and message brokers are typical building blocks for this “event thinking.”
2. Unified Namespace as the central backbone
Treat the Unified Namespace as the center of the integration architecture. OT systems publish states and events to the UNS instead of keeping data in silos or sending it directly to SAP. SAP, MES, analytics, and maintenance systems consume the relevant information based on their roles. A clear topic structure and access control keep the namespace manageable. This allows new applications to be connected later without building new point-to-point interfaces. Further information can be found here.
3. Combine edge and cloud intentionally
Not all processing belongs in SAP or in the cloud. Process raw data as close to the source as possible: filter, aggregate, contextualize—then forward. An i-flow Edge can analyze high-frequency signals locally and derive events or KPIs from them. These results are then delivered via the UNS to SAP or other cloud services. This reduces data volume, relieves network load, and lowers cloud costs.
4. Consider security and governance from the outset
OT–IT integration requires a clear security and operating model: outbound-only connectivity from OT, certificate-based connections (e.g., MQTT/TLS, OAuth for APIs), and consistent network segmentation. In addition, establish business governance: define which data flows to SAP, with what quality and granularity; assign least-privilege permissions for technical users; and implement a joint change process between IT and OT. Further information can be found here.
Guideline for cloud SAP: Avoid direct point-to-point connections from the cloud to the shop floor. Instead: OT → local UNS (e.g., i-flow) → selected events into SAP (e.g., via MQTT/AMQP).
5. Modernize incrementally instead of rebuilding everything
Avoid replacing IDoc or RFC integrations “in one big bang.” Incremental modernization has proven effective: legacy interfaces continue to run reliably, while event- and UNS-based flows are introduced step by step. This reduces risk and keeps the target architecture (UNS-centric, cloud-ready) manageable. Define this target architecture clearly and align new investments (machines, software) with it from the start.
Use Cases and Customer Examples
The following examples illustrate typical customer scenarios and their implementation using the i-flow Unified Namespace (UNS).
1. Production orders & confirmations
Production orders are the central clock generator between ERP and the shop floor and must be distributed consistently, up-to-date and decoupled to all systems involved.
- SAP → i-flow (OData): i-flow periodically synchronizes production orders from SAP (e.g., aligned with planning or shift cycles) and stores them in a structured form within the UNS.
- Status change → Event in UNS: When an order is released or modified in SAP, i-flow generates a domain event in the UNS (e.g., ProductionOrderReleased).
- UNS → i-flow Edge → System: The i-flow Edge subscribes to the event, retrieves the associated order data from the UNS, and transfers it OT-close to the production line or control system.
- Confirmation → UNS → SAP: Production confirmations are published by the Edge as events. i-flow selectively posts the relevant confirmations back to SAP via OData or BAPI.
What is important: SAP remains the transactional system of record, the i-flow UNS distributes events, and shop floor systems remain fully decoupled.
2. Machine data & KPIs
Machine data provides the foundation for transparency, performance indicators, and optimization based on cycle times, counters, temperatures, and machine states. However, this data generates volumes that should not be sent unfiltered to the cloud—if only for cost reasons.
- Machine → i-flow Edge → UNS: Machine and process data is continuously collected by the i-flow Edge and published to the UNS as raw signals or state events.
- Aggregation at the Edge/UNS:The i-flow Edge derives aggregated values, KPIs, or technical events from raw data (e.g., ShiftOutputCalculated, DowntimeDetected).
- UNS → SAP (OData/BAPI): Only aggregated KPIs or business-relevant events are posted transactionally to SAP.
What is important: Raw data remains outside SAP; SAP consumes results. ERP systems are not designed as time-series databases. For advanced analytics scenarios, machine data can be forwarded directly to SAP Digital Manufacturing Insights via MQTT.
3. Quality data & traceability
Quality and traceability data are critical for safety, compliance, and auditability. Using i-flow, companies capture quality measurements such as dimensions or defect codes, log inspection results in an audit-proof manner, and track serial numbers seamlessly across the entire production chain.
- Inspection → i-flow Edge → UNS: Quality and traceability events (e.g., QualityCheckPassed, SerialAssigned) are generated at test stations or machines and published to the UNS via the i-flow Edge.
- Data enrichment in i-flow: i-flow enriches OT data (measurements, station, timestamp) with contextual SAP information such as production order, material number, serial number, or batch. This creates a complete, business-relevant quality context clearly linked to a specific product and order.
- UNS → SAP QM (OData/BAPI):Based on this enriched context, i-flow writes consistent inspection and decision data transactionally to SAP QM—for example via BAPI_QM_RESULT_RECORD (inspection lot, results, usage decision).
What is important: SAP QM receives decision-relevant, contextualized quality data. The UNS ensures decoupling, while i-flow handles the enrichment of OT data with SAP context.
4. Maintenance Data & Maintenance (SAP EAM)
Condition-based maintenance requires raw machine signals to be translated into actionable maintenance processes.
- Condition data → i-flow Edge → UNS: Sensor and condition data is continuously collected and published to the UNS.
- Evaluation at the Edge: The i-flow Edge detects threshold violations or anomalies and generates maintenance events (e.g., ConditionThresholdExceeded).
- UNS → SAP EAM (OData/BAPI):Based on these events, i-flow triggers appropriate SAP EAM objects such as measurement documents, maintenance notifications, or work orders.
What matters: SAP reacts to evaluated, meaningful events—not to raw sensor data.
Conclusion
In production environments, there is rarely a true “one-size-fits-all” integration approach. Instead, a resilient architecture is achieved through a deliberate combination of SAP interfaces tailored to each data flow: master data is typically packaged and synchronized in a robust manner (e.g., via IDocs or APIs), transactional data is posted with full transactional integrity (OData or BAPI), and events are distributed using broker-based mechanisms (Event Mesh / UNS). In modern UNS-based architectures, events form the integration backbone, while SAP consumes only business-relevant state changes via APIs or BAPIs. The appropriate integration approach is determined using clear criteria: latency requirements, data volume, degree of coupling, and the operating model (cloud vs. on-premise).